Less Work, More Output
Insight for: Developers

Maintaining an online presence often forces companies to build multiple websites, with a site for each brand, product, or country. Keeping up with dozens or even hundreds of websites can quickly turn into an expensive, time-consuming effort.
Luckily, Drupal is here to help. Multisite functionality is built into Drupal.
A Drupal multisite provides you the opportunity to create multiple websites using the same codebase. With that said, all sites would be different from one another, serving different audiences. The cost of managing a multisite platform is substantially lower than that of managing hundreds of separate websites.
At Drupal, we have several ways to accomplish multisite functionality. The following case study will describe some architectures that make this possible. Read on to identify which option is best tailored to your needs.
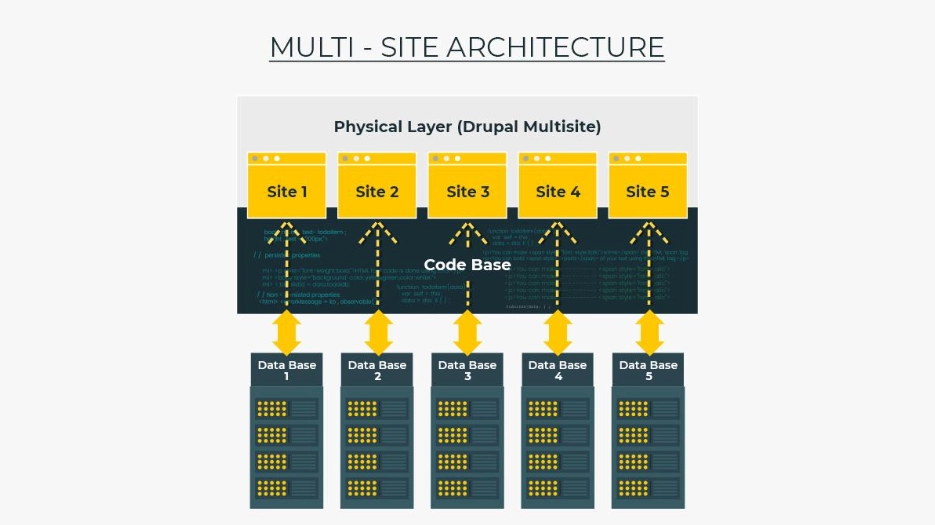
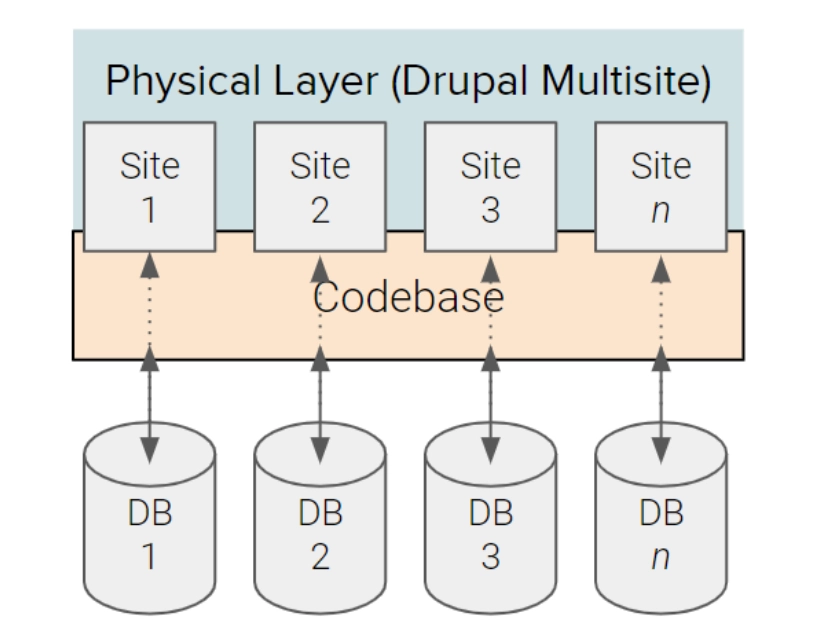
Websites share code (the Drupal core, modules, and themes), but each website has its own database so they do not share content, configuration, or settings. Each website can also contain some extra modules/themes under its own subdirectory in the same codebase. A multisite is accomplished by creating different folders for the various websites in the /sites/ folder of the Drupal system.
For example:
/sites/Site 1/
/sites/Site 2/
/sites/Site n/
We can control which website will use which modules and themes by placing them in the correct folders, accessible only for specific sites.
Classic Drupal Multisite would be most beneficial if all sites have the same features and are using similar modules and settings, but have different content and users.
A company maintains many brands, and each brand requires a website. Websites must be visually different (each brand has its own guidelines), but functional requirements are mostly the same (banners, videos, sliders, contact forms, etc.). The same development team develops and maintains all sites, but each site may have its own marketing or content team that manages content for the site.
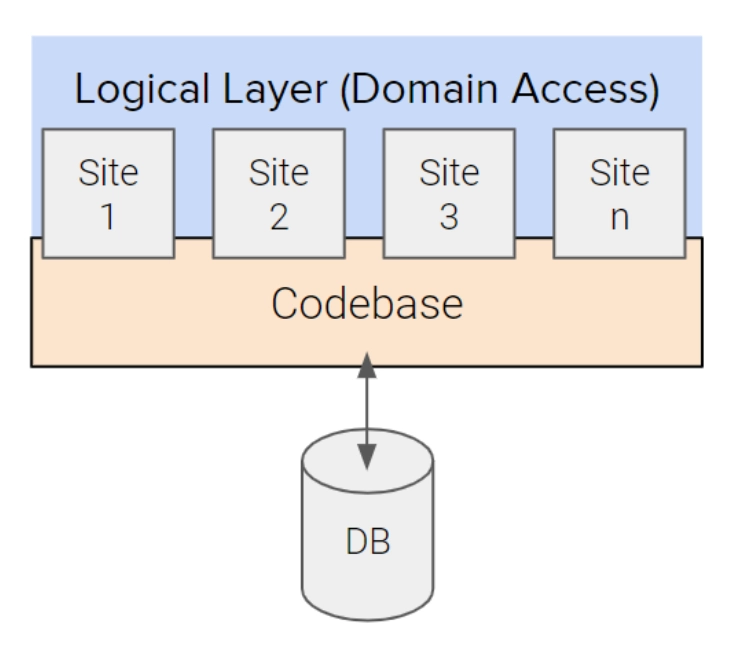
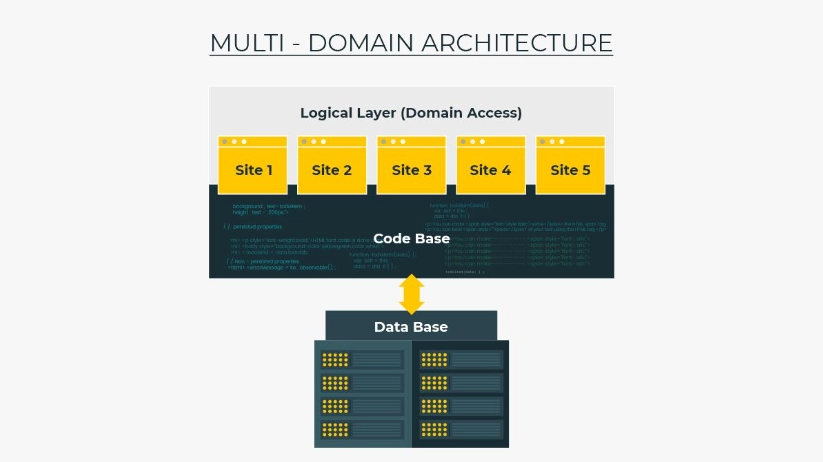
This architecture consists of a single codebase and single database/installation. The Domain Access suite of modules provides functionality that allows multiple sites (domains) to be served from this setup. It also allows you to categorize your content as shared or unique. If you like, you can choose a specific piece of content for one particular domain, then share it across all sites.
Multi-Domain setup makes sense if sites will share content and/or users, and if all of the sites will have the same functionality and content types/data structures, but might have some slight visual differences.
It will exist as an e-commerce site with one product catalog, a single checkout, and common users, but separate domains for different product categories.
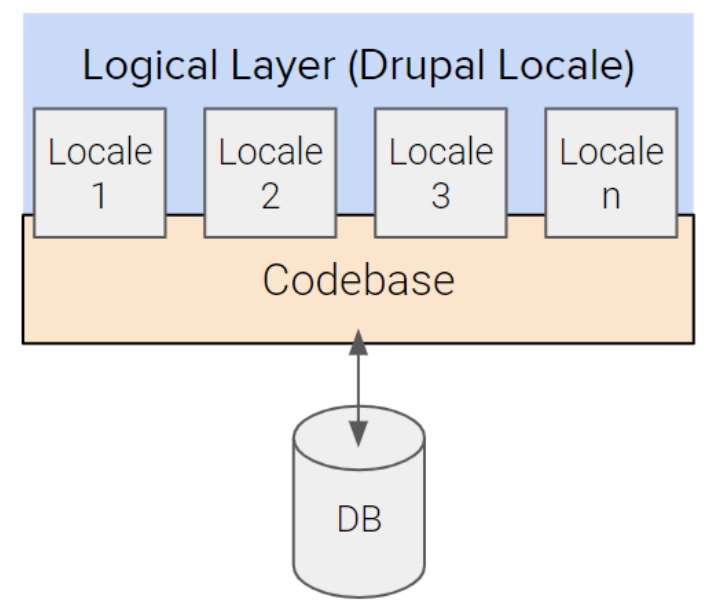
Multi-Locale allows for the use of language-based regional targeting, utilizing the power of multilingual capabilities for multiregional targeting. This is recommended for sites targeting multiple regions.
Using the Drupal multilingual system, you can translate any piece of content to different languages. The admin interface has built-in translations for 94 languages.
The domain name may be used to determine the language. Specifying "example.com" as the language domain for English and "example.de" as the language domain for German will result in content being shown only in the respective language for each domain.
Multi-Locale Architecture would be useful if you want to show content to your site visitors in their native language. Multilingual sites can dynamically show translated content to their visitors based on customizable factors like browser language.
Corporate website for small and medium-sized businesses with clients from different countries.
Drupal distribution provides everything you need to start your web projects, from the required modules and libraries to custom modules and themes, and from the configuration to the default content. It’s a website starter pack.
Drupal distribution focuses on a particular business and adds features specific to it into one installation, so it takes less time to configure the most common elements of a Drupal website.
For example, if you’re looking to build Drupal websites for hospital management, your Drupal developers can pre-configure modules for patient registrations, investigations, pharmacy management, etc., and also configure roles for admins, doctors, patients, and nurses. Now, when you want to deploy the same Drupal solution (or one similar to it) for a different hospital, much of the work is already done.
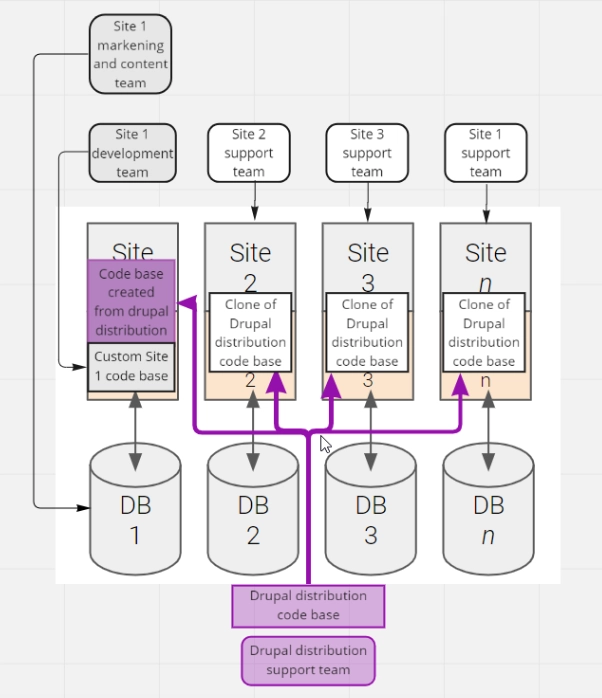
A distribution profile works well if the sites are all starting out the same but are expected to grow in different directions. Maintenance work is expected to be independent for each of the sites.
A multinational corporation maintains many brands or services, and each brand (service) requires a website in a separate country or region. Websites are visually different (each brand has its guidelines) and the languages vary across countries, but functional requirements are mostly the same (banners, videos, sliders, news, articles, contact forms, user registration and personal account, etc.). Each country has its own development and marketing or content team, which manages codebase and content for that country’s site.