Let's ask Google
Insight for: Developers

Is Drupal SEO friendly? Good question. To get to the bottom of this, let's analyze the Google recommendations for website SEO optimization and the corresponding solutions Drupal offers.
Google: The first step to getting your site on Google is to be sure that Google can find it. The best way to do that is to submit a sitemap. A sitemap is a file on your site that tells search engines about new or altered pages on your site.
Drupal: There’s a module for that: Simple XML Sitemap. Sitemaps generated by this module adhere to the new Google standard regarding multilingual content by creating hreflang sitemaps and image sitemaps. Trust us: Google bots will thank you later.
Other useful functionalities include periodic submission to search engines and the submission of any content changes to IndexNow.
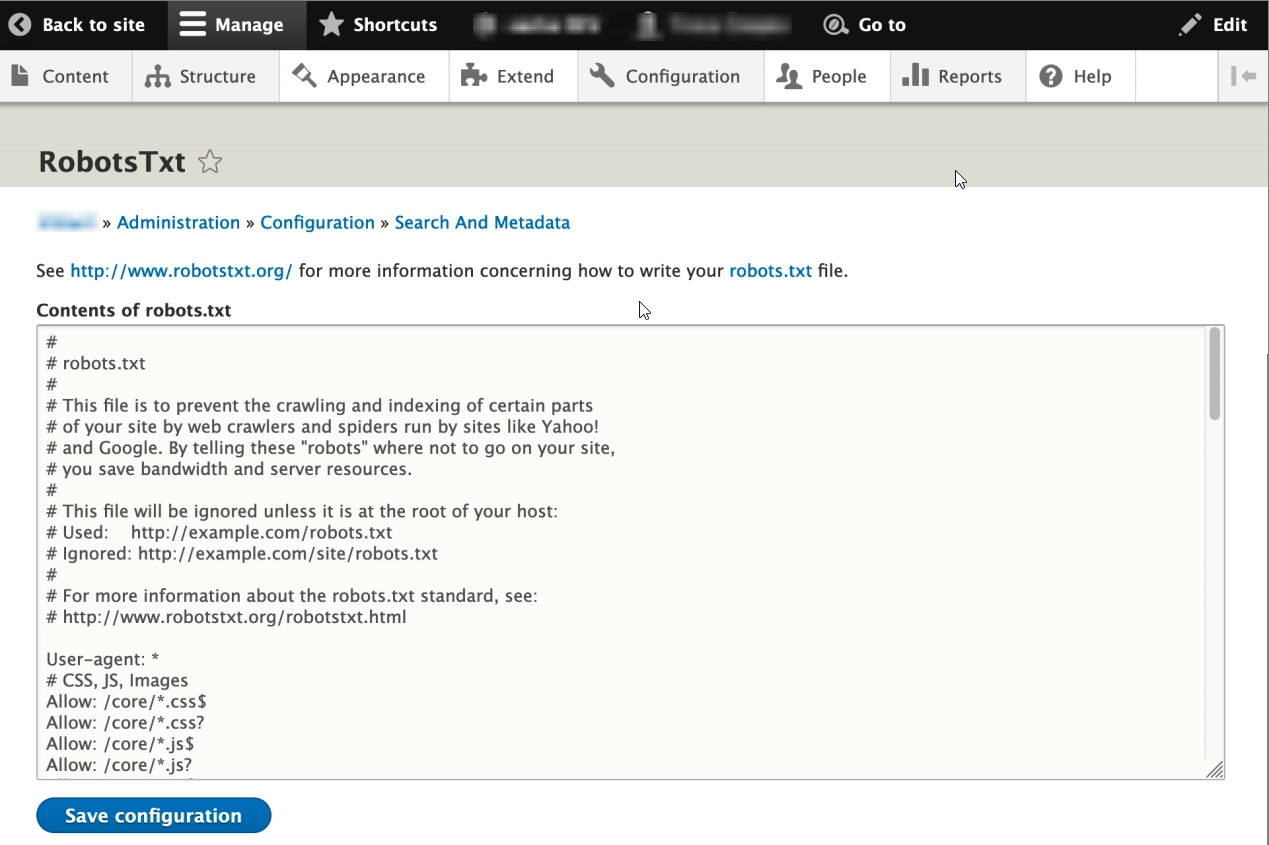
Google: Tell Google which pages you don't want crawled. For non-sensitive information, block unwanted crawling by using robots.txt. A robots.txt file tells search engines whether they can access, and therefore crawl, parts of your site.
Drupal: RobotsTxt module generates the robots.txt file dynamically and gives you the chance to edit it from the web UI.
Google: Help Google (and users) understand your content.
Place the <title> element within the <head> element of the HTML document, and create unique title text for each page on your site.
Use the meta description tag, which gives Google and other search engines a summary of what the page is about.
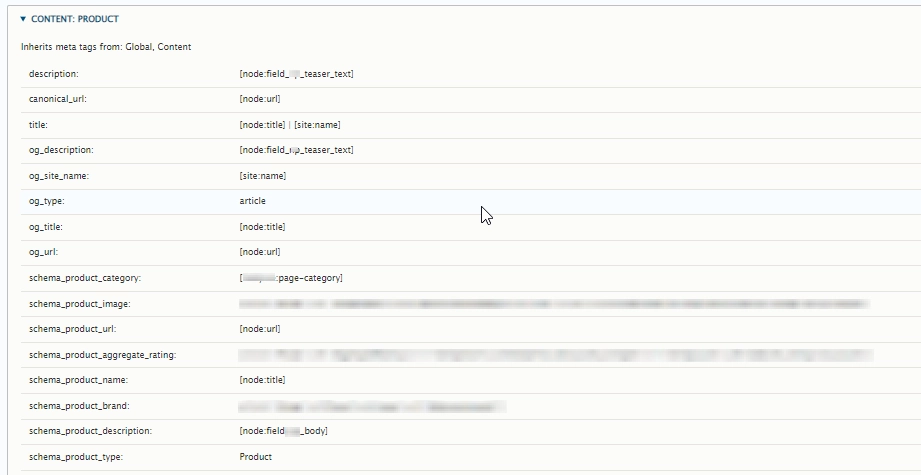
Add structured data markup. Structured data is code that you can add to your sites' pages to describe your content to search engines.
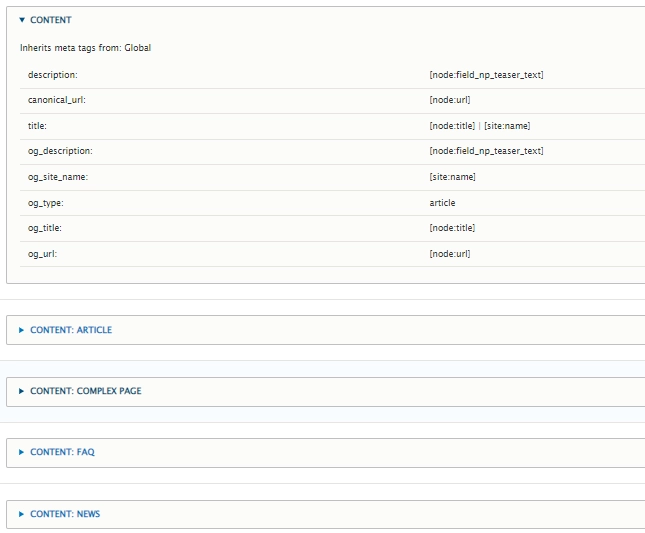
Drupal: Use Metatag module for all of these tasks to add tags from the Drupal admin interface without writing a code. It offers over 300 different meta tags for different purposes, so take a look and find the right ones for your site.
Setup of <title> and meta description tags
Setup of structured data markup for individual product page
Google: Use breadcrumb lists. A breadcrumb is a row of internal links at the top or bottom of the page that allows visitors to quickly navigate back to a previous section or the root page.
Google Search uses breadcrumb markup in the body of a web page to categorize the information from the page in search results.
Drupal: Drupal generates breadcrumbs with Google-recommended markup out of the box.
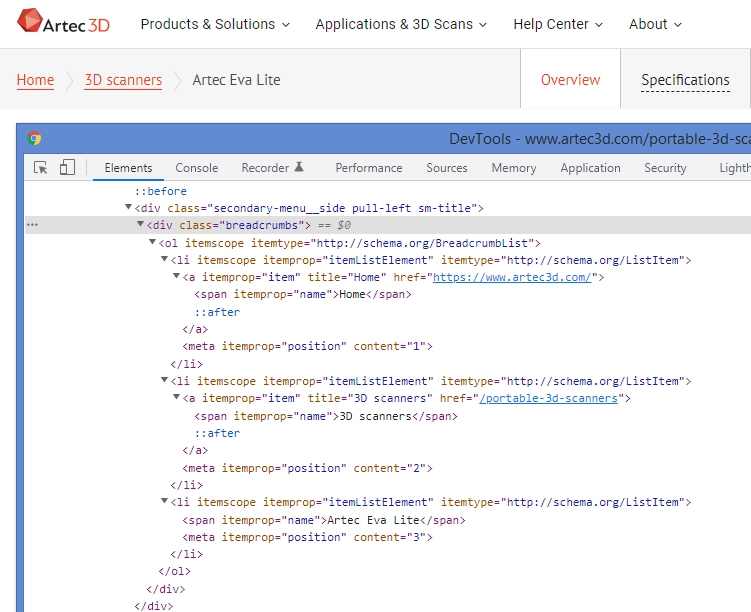
Google: Include a simple navigational page for your entire site (or the most important pages, if you have hundreds or thousands) for users.
Drupal: There’s a Sitemap module for that. This module provides a sitemap that gives visitors an overview of your site.
Google: Show useful 404 pages. Having a custom 404 page that kindly guides users back to a working page on your site can greatly improve a user's experience.
Drupal: Search 404 module performs a search using the keywords in the missing URL to select appropriate content to show to the lost visitor.
For example, if a visitor goes to https://yourDrupal9.site/animals/flying-fish (which doesn’t exist on your website) and finds nothing there, then this module will search for “animals flying fish” and display those search results below the “404 Page Not Found” error message.
Google: Simple URLs convey content information. URLs with words that are relevant to your site's content and structure are friendlier for visitors navigating your site.
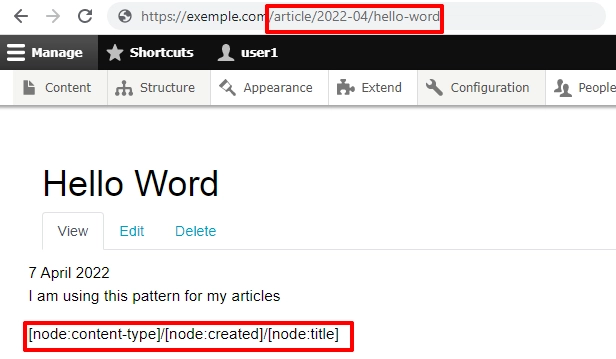
Drupal: Clean URLs (in Drupal core and enabled by default in Drupal 9) and Pathauto modules will help you to follow this recommendation.
The Pathauto module automatically generates URL/path aliases for various kinds of content without requiring the user to manually specify the path alias. The aliases are based upon a "pattern" system using tokens that the administrator can change.
Google: Provide one version of a URL to reach a document. If you find that people are accessing the same content through multiple URLs, set up a 301 redirect from non-preferred URLs to the dominant URL.
Drupal: The Redirect module redirects visitors from old URLs to new URLs. When you move a piece of content to another section of your site or inadvertently change the URL, this module can really help. The Redirect module highlights the power of Drupal, automating what was once an arduous and ongoing SEO chore. Thanks to the power of Drupal and the Redirect module, fixing links is a much less frequently needed task.
Google: Use links wisely - write good link text. Link text is the visible text inside a link. This text tells users and Google something about the page you're linking to.
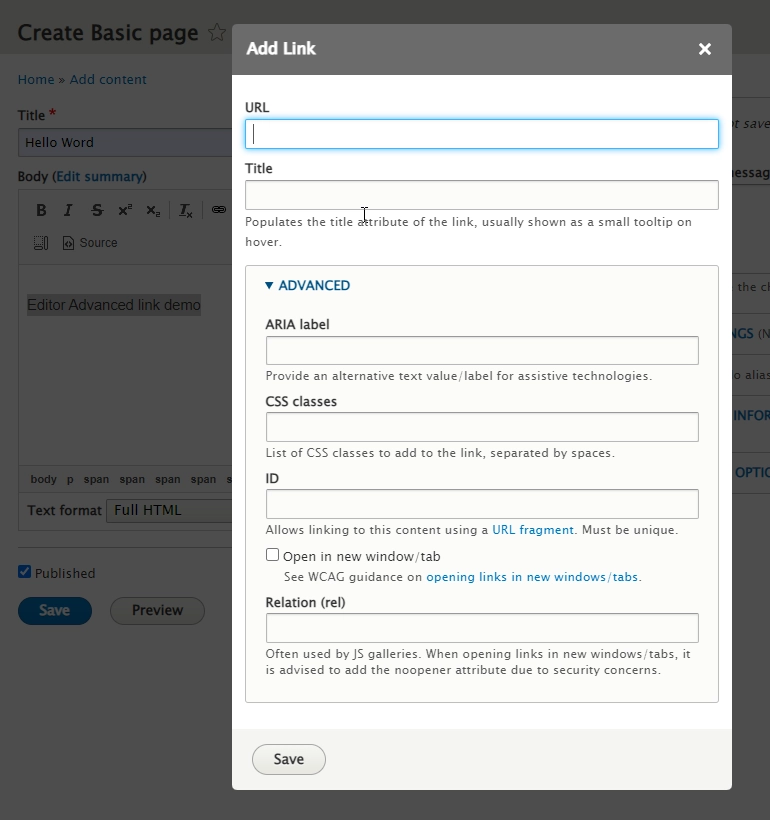
Drupal: The Editor Advanced link module allows you to define title, class, ID, target, and rel for links in CKEditor.
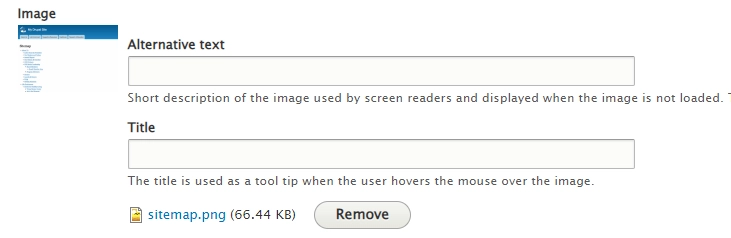
Google: Use the alt attribute and Title for images.
Drupal: You can add alt attribute and Title text for each image added to content from the Drupal administrative interface out of the box.
Google: Analyze user behavior on your site. Google Analytics is a valuable source of insight for this.
Drupal: Google Analytics module adds the Google Analytics statistics features to your site.
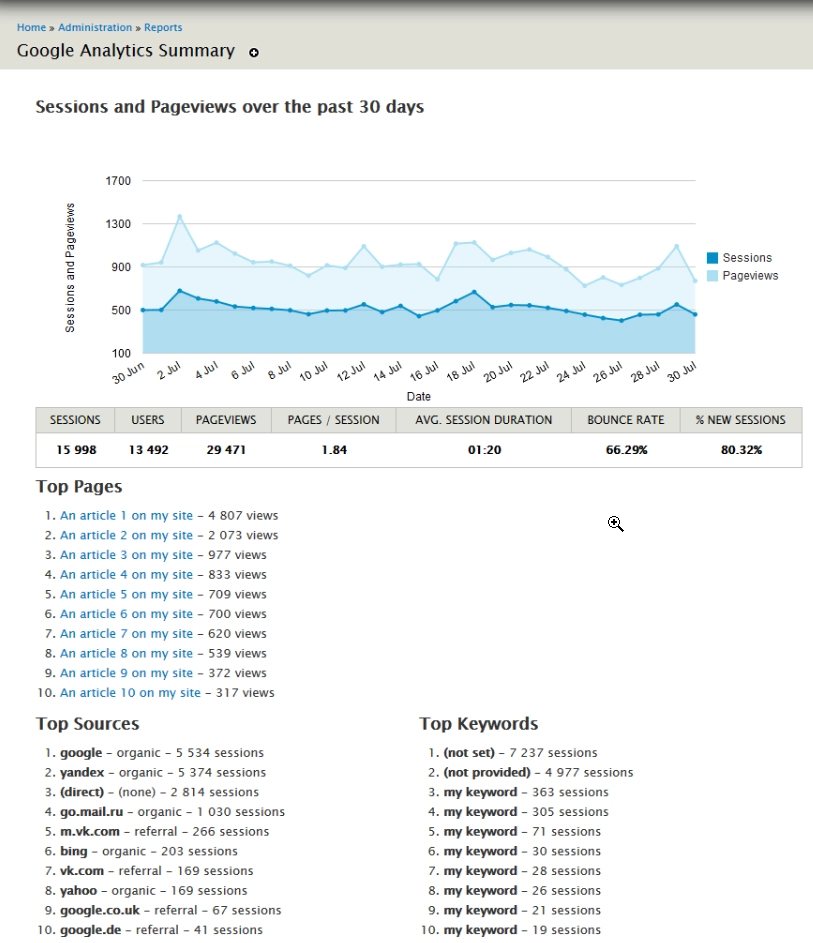
Google Analytics Reports module provides graphical reporting of your site's tracking data directly from the Drupal administrative panel.
The fact that Drupal CMS is SEO friendly does not mean that a site built with Drupal automatically becomes SEO friendly (although there is some truth in this).
It simply means that Drupal offers all the necessary tools an SEO specialist can use to make the site comply with recommendations from Google and other search engines.
Drupal SEO checklist module will help with this. The module doesn’t add any specific functionality, but it is a great assistant that makes sure your website is properly SEO optimized. It provides a list of tasks to accomplish and modules to install. Links to the associated modules are attached to each task.
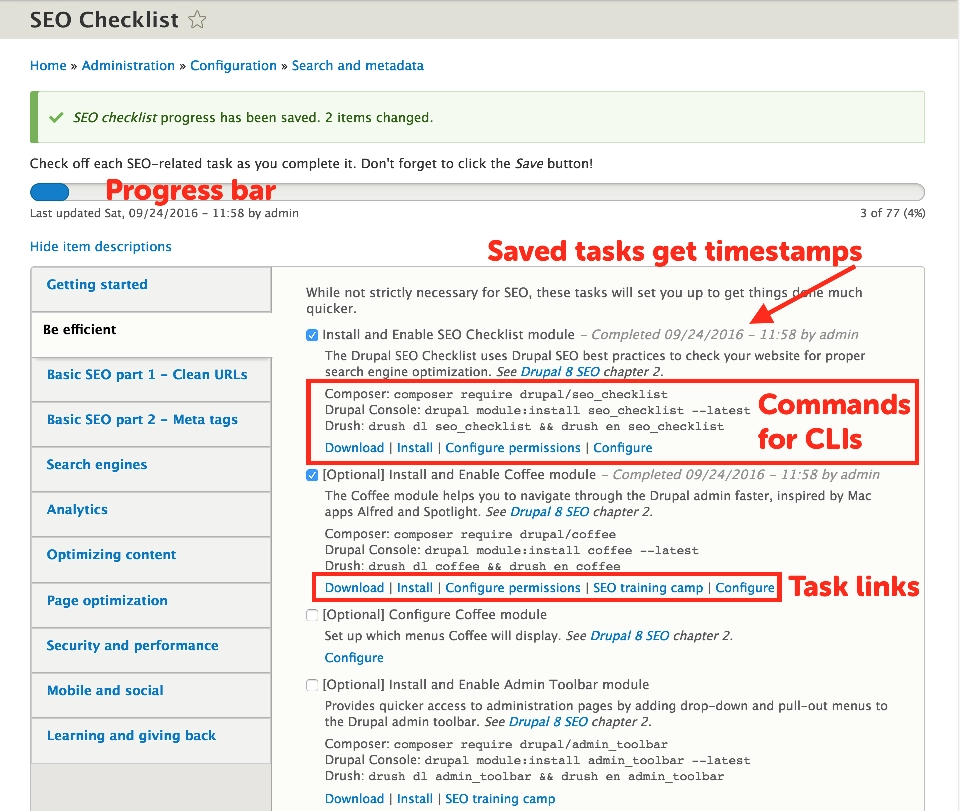
This module automates most of the on-page optimization, making use of the latest techniques, which are updated in the module regularly. The SEO checklist module, however, is not for newbies, as it requires the user to know the basics of SEO to make optimal use of it.